CETIR Ascires, a leading Catalan medical team specialized in Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine, has become a pioneer in the field of virtual liver biopsies.
Through the development of proprietary biomarkers, they have been able to diagnose liver pathologies without the need to perform invasive biopsies on patients.
Inflammation, fat accumulation in the liver, fibrosis or iron overload are indicators associated with various liver diseases.
Cetir Ascires has been one of the pioneers in the introduction of this technique in Catalonia.
The Spanish Association for the Study of the Liver (AEEH) warns about the increase of liver problems in the Spanish population, especially related to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Surprisingly, fast food abuse and sedentary lifestyles have become the leading cause of cirrhosis in the country, surpassing alcohol consumption.
The intake of fast food and processed products is having a significant impact on the development of liver disease, which makes early detection even more crucial.
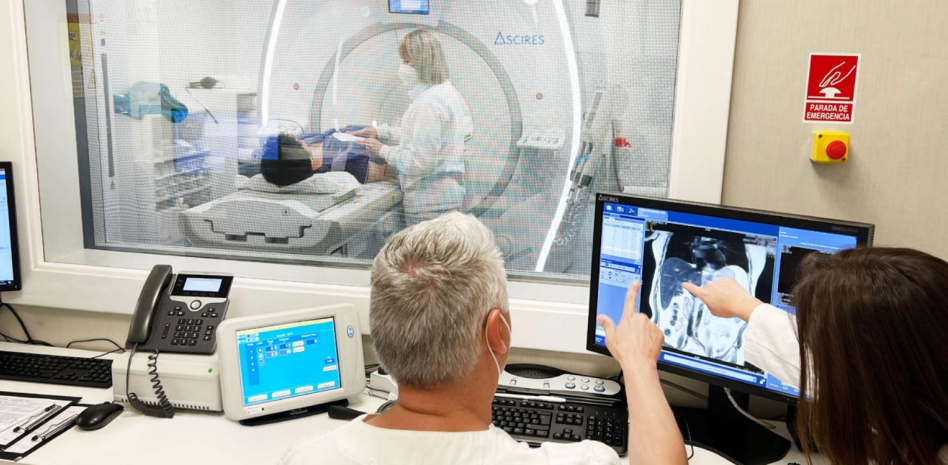
How virtual liver biopsies are performed
Using advanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) sequences and an innovative technique called elastography, they have succeeded in creating a tool called HepaTools, which generates a kind of virtual biopsy of the liver.
Elastography consists of applying low-intensity vibrations to the abdomen, which makes it possible to obtain a visual map of the liver and determine its degree of stiffness.
This information is crucial to establish whether the liver presents normal levels, inflammation, fibrosis or cirrhosis, which facilitates the early diagnosis of liver pathologies.
Assessing these levels is critical for early diagnosis and management of conditions such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and other metabolic or autoimmune disorders.
However, conventional biopsies, which are the reference test for analyzing these parameters, are invasive, require hospital admission and carry risks of complications.
To avoid these inconveniences, the Ascires R+D+i Department (AsciresLab) has developed biomarkers that allow these values to be analyzed by means of non-invasive and painless imaging tests for the patient.
The advantage of HepaTools is that it provides an accurate and quantitative assessment of liver parameters in the whole organ, unlike conventional biopsy which only analyzes a small tissue sample.
It also avoids the risks and complications associated with invasive biopsies.
Project in validation phase
The project has reached preclinical validation with the publication of the imaging biomarkers in the journal Diagnostics.
It is currently in the clinical validation phase in collaboration with the Health Research Institute (INCLIVA), where it is working with patients diagnosed with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
The ultimate goal is to develop a computer algorithm to diagnose liver diseases.